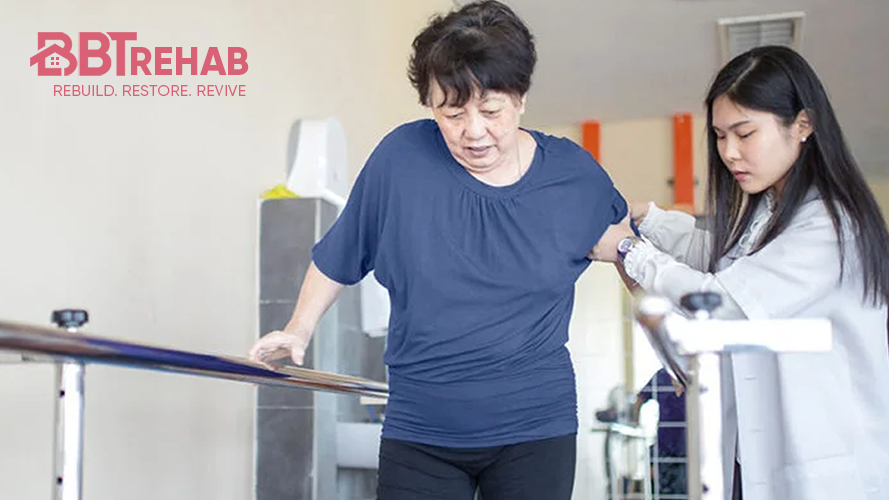
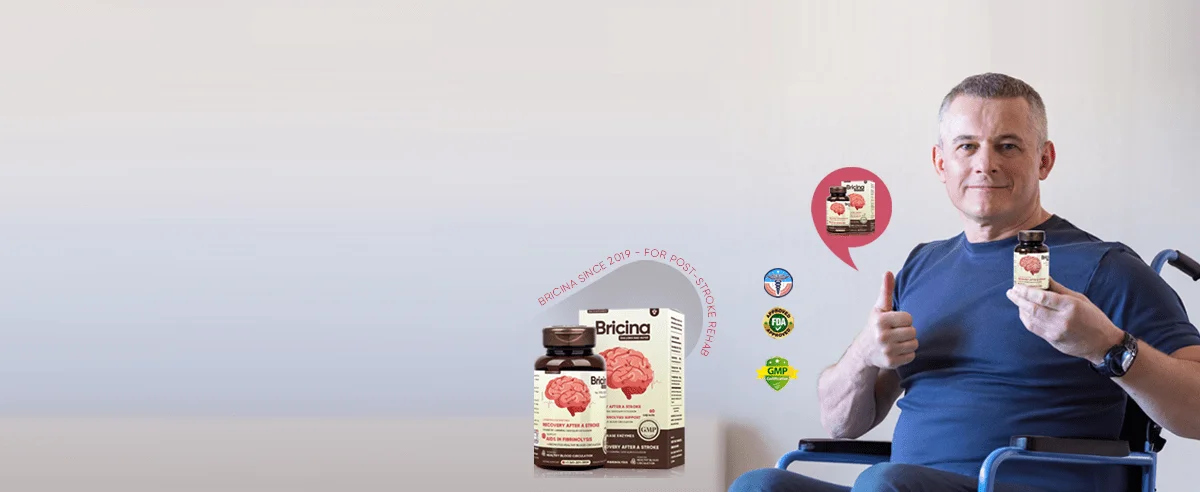
BBT Rehab with Bricina is a combined home-based neurorehabilitation approach that pairs structured, task-specific rehabilitation protocols with adjunctive Bricina supplementation.
This document summarizes the putative mechanisms of action, proposed clinical effects, suggested treatment protocol, outcome measures, contraindications, safety considerations, and recommendations for clinical evaluation. The aims are to provide clinicians and institutional partners a clear, medically oriented overview suitable for evaluation, implementation, or further study.
Background
Stroke is a major cause of long-term neurological disability worldwide. Recovery depends on timely intervention, intensive rehabilitative training, and the brain’s capacity for neuroplastic change. Interventions that combine behavioral training with agents that support neuronal repair and neurovascular health may enhance functional recovery compared with rehabilitation alone.
Proposed Mechanisms of Action
- Enhancement of neuroplasticity: Bricina is proposed to facilitate synaptogenesis and dendritic remodeling, increasing the ability of peri-infarct and contralesional cortical areas to form functional connections that substitute for damaged networks.
- Neuroprotective and metabolic support: Bricina may reduce secondary neuronal injury by modulating oxidative stress pathways and supporting mitochondrial function, thereby preserving penumbral tissue and improving neuronal resilience.
- Improved cerebral microcirculation: By supporting endothelial function and microvascular perfusion, Bricina could enhance delivery of oxygen and nutrients to recovering neural tissue, promoting survival and function of at-risk neurons.
- Augmentation of synaptic transmission: The compound may modulate neurotransmitter systems and receptor expression that are critical for relearning motor, language, and cognitive tasks.
Clinical Effects Observed or Hypothesized
- Motor recovery: Faster gains in voluntary movement, improved coordination, and increased active range of motion when Bricina is provided alongside repetitive, task-specific physiotherapy.
- Speech and language: Enhanced progress in expressive and receptive language functions when combined with targeted speech therapy.
- Cognitive domains: Improvements in attention, working memory, and processing speed during the subacute and chronic phases of stroke rehabilitation.
- Functional independence: Higher scores on global functional scales (e.g., modified Rankin Scale, Barthel Index) and improved activities of daily living (ADL) performance are anticipated with a combined approach.
Treatment Protocol (Suggested Clinical Framework)
General principles: Combine structured rehabilitation (physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy as indicated) with a standardized Bricina supplementation schedule. Begin as early as clinically feasible after medical stabilization, as early intervention typically yields better neuroplastic outcomes.
- Patient selection:
- Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke patients after acute stabilization.
- Patients with residual motor, speech, or cognitive deficits who are medically stable and can participate in therapy.
- Exclude individuals with contraindications listed below.
- Bricina administration (example regimen):
- Loading phase: oral supplementation daily for the first 4 weeks (dose and formulation to follow manufacturer/medical guidance).
- Maintenance phase: reduced daily dosing for subsequent months (commonly 2–6 months depending on clinical response and tolerance).
- Treatment duration: minimum recommended trial of 12 weeks to assess early functional gains; many patients may continue for 6 months under clinical supervision.
- Rehabilitation regimen:
- Intensity: task-specific practice at least 5 days/week, with sessions totaling 60–90 minutes/day where feasible.
- Content: repetitive motor training, constraint-induced movement therapy or modified approaches, gait training, balance work, and language/cognitive exercises tailored per patient.
- Progression: graded difficulty, objective tracking, and periodic reassessment every 4 weeks.
- Monitoring:
- Baseline and periodic neurological exams, functional outcome scales, and cognitive testing.
- Monitor for adverse effects, vital signs, and any laboratory parameters recommended by the product safety profile.
Outcome Measures (Recommended)
- Primary functional measures:
- Modified Rankin Scale (mRS)
- Barthel Index (BI)
- Fugl-Meyer Assessment (motor domains)
- Speech & language:
- Boston Naming Test or language subscales relevant to local practice
- Cognitive assessment:
- Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) or Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)
- Quality of life and caregiver burden:
- Stroke-specific quality-of-life instruments
- Objective measures:
- Gait speed, grip strength, timed up-and-go (TUG)
Safety, Contraindications & Interactions
- Safety: Use only products from verified manufacturers with clear composition and safety data. Record and report adverse events systematically.
- Contraindications (general examples):
- Known hypersensitivity to any component of the supplement.
- Uncontrolled medical comorbidities (e.g., unstable cardiac disease) until stabilized.
- Potential interactions: Evaluate concomitant medications for interactions—particularly agents affecting platelet function, anticoagulants, or drugs altering cerebral blood flow. Consult pharmacology references and the patient’s treating physician.
- Pregnancy and lactation: Use only if benefits justify potential risks and after specialist consultation.
Evidence and Research Recommendations
Current evidence: Clinical experience and preliminary observational data may suggest benefit when Bricina is combined with intensive rehabilitation, but high-quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are required to quantify efficacy and safety definitively.
- Suggested study designs:
- Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials with stratification by stroke severity and time since stroke.
- Primary endpoints: change in Fugl-Meyer motor score and functional independence measures at 3 and 6 months.
- Secondary endpoints: cognitive scores, language outcomes, quality of life, neuroimaging biomarkers (e.g., functional MRI or diffusion metrics) when feasible.
- Biomarker and mechanistic studies: Investigate changes in neurotrophic factors, inflammatory markers, and perfusion parameters to elucidate biological effects.
Implementation Considerations for Clinical Practice
- Multidisciplinary coordination: Neurologists, physiatrists, physical therapists, speech therapists, pharmacists, and nursing staff should collaborate on treatment plans and monitoring.
- Patient & caregiver education: Provide clear instructions on supplement use, expected timelines, home exercise protocols, and warning signs that require medical attention.
- Documentation: Maintain structured clinical records including baseline function, dosing schedule, adverse events, and periodic outcome assessments.
- Quality control: Source Bricina from regulated suppliers and maintain chain-of-custody documentation for clinical use or studies.
Conclusion
BBT Rehab with Bricina represents a rational, dual-modality strategy that couples behavioral rehabilitation with adjunctive biological support. While the mechanistic rationale is consistent with contemporary neurorehabilitation principles—enhancing neuroplasticity, protecting vulnerable neurons, and improving microvascular support—rigorous clinical trials are necessary to establish the magnitude of benefit, optimal dosing, timing, and long-term safety. Clinicians considering implementation should do so within a multidisciplinary framework, with careful patient selection, monitoring, and documentation.
Suggested References & Further Reading
- Recommended: Reviews on neuroplasticity and post-stroke rehabilitation, guidelines from major stroke societies on rehabilitation timing and intensity, and standard texts on neuropharmacology of recovery-enhancing agents (insert institutionally preferred citations).
- Note: Include product-specific safety data sheets, published clinical studies if available, and regulatory documentation when preparing institutional protocols or consent forms.




















 Every component undergoes rigorous safety and performance checks, ensuring stroke survivors receive a trusted and effective home-based rehabilitation solution.
Every component undergoes rigorous safety and performance checks, ensuring stroke survivors receive a trusted and effective home-based rehabilitation solution.