Post - Stroke RehabilitationWhat causes ischemic stroke and how to treat ?
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot or other blockage restricts blood flow to the brain, depriving it of oxygen and nutrients.
Treatment focuses on restoring blood flow, often with medications like tPA to dissolve clots, or procedures to physically remove them.
Causes of Ischemic Stroke:
Blood Clots:
These can form in the heart (especially with atrial fibrillation) or in the arteries supplying the brain and travel to block a smaller vessel.
Atherosclerosis:
Fatty deposits (plaque) build up in the arteries, narrowing them and increasing the risk of clot formation or blockage.
Other Factors:
Conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart conditions, and blood disorders can also contribute to the risk of ischemic stroke.
Treatment for Ischemic Stroke:
Thrombolytics (tPA):
Medications like tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) are used to dissolve blood clots and restore blood flow.
Mechanical Thrombectomy:
A catheter is used to navigate to the blockage and physically remove the clot.
Other Medications:
Blood thinners like aspirin or other antiplatelet drugs can be used to prevent future clots.
Surgery:
Procedures like carotid endarterectomy (removing plaque from the carotid artery) or stenting may be used to improve blood flow and prevent future strokes.
Rehabilitation:
Physical, occupational, and speech therapy may be needed to help with recovery and functional limitations.

Common Challenges After a Stroke: Physical, ...
Home Exercise For Stroke Patients | As ...

POST-STROKE 6 months of sustained ...

How Long Does it Take to Recover After a ...
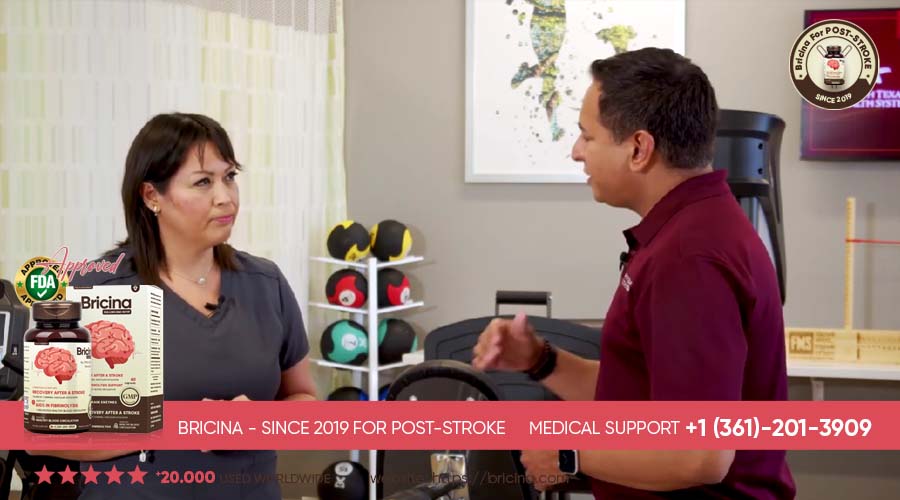

Help Reduce Your Risk of Stroke by ...

Stroke - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment ...

6 Warning Signs of Stroke You Should know
Understanding the Different Types of Stroke








